The Importance of Liver Fluke-Fasciola Control in Livestock

Livestock health is a paramount concern for farmers and caretakers, and one persistent threat is liver fluke infestation caused by Fasciola. In this article, we explore the critical importance of controlling liver flukes in livestock for overall well-being and productivity.
Understanding Liver Fluke-Fasciola

Liver fluke, scientifically known as Fasciola, is a parasitic flatworm that can wreak havoc on the liver of various livestock species, including cattle, sheep, and goats. Understanding its life cycle is crucial to implementing effective control measures.
Impact on Livestock Health
Liver fluke infestation can have severe consequences on the health of livestock. From reduced productivity to compromised growth rates and reproductive issues, the impact on the overall well-being of animals cannot be overstated.
Economic Implications
Beyond the immediate health concerns, liver fluke infestation carries economic ramifications. Losses in productivity and the cost of treatment contribute to a significant financial burden for livestock owners.
Transmission Routes
Livestock can contract liver fluke through contaminated pastures and water sources. Understanding the routes of transmission is key to preventing the spread of infestation within a herd.
Important query
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Where is liver fluke most common? | Liver fluke is most common in regions with a warm and humid climate. It is often found in areas with moderate temperatures (10 to 25 degrees Celsius), high humidity, and freshwater bodies. |
| Common Name for Liver Fluke | Liver fluke |
| Location of Fasciola | Fasciola hepatica, a common liver fluke species, is found globally in regions meeting the environmental criteria for its life cycle. This includes parts of Europe, Asia, Africa, and the Americas. The presence of suitable intermediate hosts (snails) and environmental conditions conducive to the parasite’s life cycle influence its distribution. |
Liver Fluke Cases in Bihar
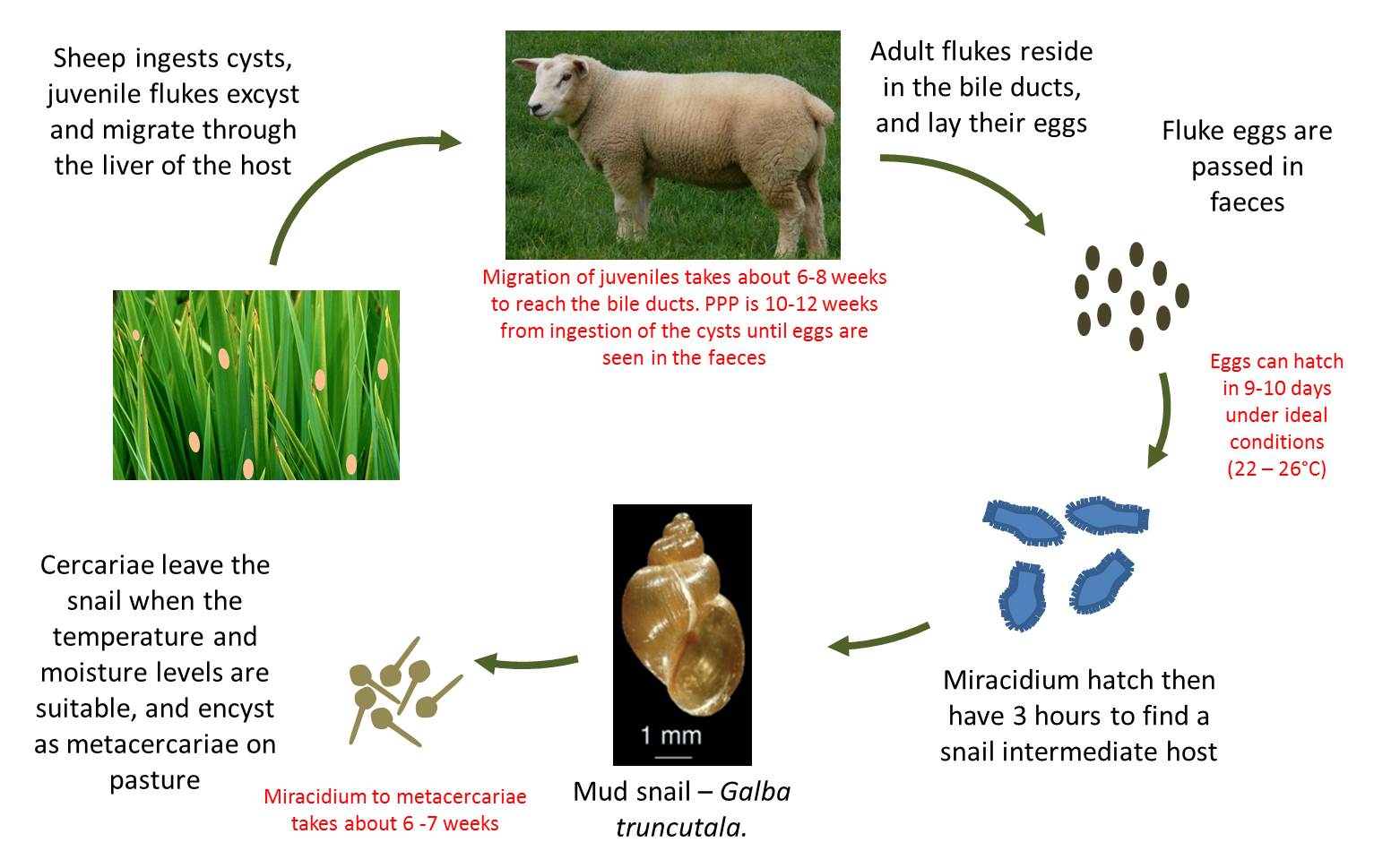
If there are reported cases of liver fluke in Bihar, it may indicate that the environmental conditions and factors necessary for the transmission of liver fluke are present in the region. Understanding the local ecology and implementing control measures, such as improved sanitation and animal husbandry practices, can be crucial in managing the spread of liver fluke infections. Affected communities need to work with healthcare professionals and public health authorities to address the issue effectively.
Prevention Strategies

Pasture Management
Maintaining clean and uncontaminated pastures is a foundational step in preventing liver fluke infestation. Dr. Munna Singh recommends strategic pasture management practices to reduce the risk.
Strategic Deworming
Regular and strategic deworming is essential for controlling liver fluke. Dr. Munna Singh’s recommended deworming protocols, including timing and frequency, are crucial for effective prevention.
Water Quality Control
The role of water sources in liver fluke transmission cannot be overlooked. Implementing practices to ensure clean water for livestock is integral to control efforts.
Treatment Options
In cases where liver fluke infestation is detected, prompt and effective treatment is vital. Consulting with a veterinarian for proper diagnosis and tailored treatment is recommended.
Case Studies
Real-life examples underscore the importance of liver fluke control. Successful cases of prevention and treatment serve as valuable lessons for livestock owners.
Drawing from years of expertise, Dr. Munna Singh provides insights into liver fluke control. His perspective on developing effective strategies adds a layer of practicality to the implementation of control measures.
Expert Insights by Dr. Munna Singh
The importance of liver fluke-fasciola control in livestock cannot be overstated. By understanding the risks, implementing preventative measures, and seeking expert guidance, livestock owners can safeguard the health and productivity of their herds.
Liver fluke, specifically Fasciola hepatica, can infect a variety of mammals, including humans. Here are the details regarding the potential hosts for liver fluke
| Host Type | Hosts | Role in Life Cycle |
|---|---|---|
| Definitive Hosts | Cattle, Sheep, Goats, and other herbivorous mammals | Adult liver flukes reside in the bile ducts, reproduce, and release eggs in the host’s liver. |
| Intermediate Hosts | Freshwater snails, e.g., Lymnaea truncatula, Lymnaea aviatrix | Miracidia hatch from eggs in water, infect snails, and go through developmental stages (sporocysts, rediae, and cercariae). |
| Transport Hosts | Various plant-eating animals (e.g., rodents) | Ingest contaminated vegetation containing metacercariae, serving as hosts for immature stages. |
| Accidental Hosts | Humans and other mammals | Ingest metacercariae in contaminated water or aquatic plants, leading to infection in the liver. |

I’m Shweta Bharti, and I’m not just a blogger; I’m a storyteller with an unending love for Bihar. Bihar is not just my home; it’s my muse. I was born and raised in the heart of this culturally rich state, and that’s where my journey as a writer began.My passion is to share the beauty and depth of Bihar through my words. Bihar isn’t just a place; it’s a treasure trove of history, traditions, and untapped potential. Through my blog, BiharLinks.com, I aim to change perceptions and uncover the hidden gems of Bihar.